Unsere Praxis
… liegt zentral, mitten im Geschäftszentrum von Stuttgart. Die Umgebung ist bunt und lebendig. „Königstraße“ – mehr Mitte geht nicht.
Unsere Klientel ist international und der Großteil unserer Patientinnen ist jung und berufstätig. Mit modernen Räumen, freiem W-LAN, durchgehenden Öffnungszeiten und der Möglichkeit, online Termine zu buchen, möchten wir den besonderen Ansprüchen an eine Großstadtpraxis gerecht werden.
Für unsere Patientinnen stehen je nach Alter und persönlicher Lebenssituation unterschiedliche Bedürfnisse im Vordergrund.
Im Allgemeinen begegnen wir folgenden Aussagen:
„Ich möchte nicht schwanger werden.“
„Ich will schwanger werden.“
„Ich bin schwanger.“
Kurz und knapp: Alles dreht sich um Kind nein oder Kind ja.
Empfängnisverhütung und Mutterschaftsvorsorge stehen damit im Zentrum unserer ärztlichen Betreuung.
Im Bereich Verhütung haben wir uns auf die Einlage von Spiralen spezialisiert und können so der steigenden Nachfrage nach hormonfreier Verhütung gerecht werden. Wir haben alle gängigen Modelle vorrätig und bieten die Einlage auch für externe Patientinnen an. Wenn Sie an einer Spiraleneinlage interessiert sind, schicken Sie uns am besten eine Nachricht, damit wir die weitere Vorgehensweise direkt klären können.
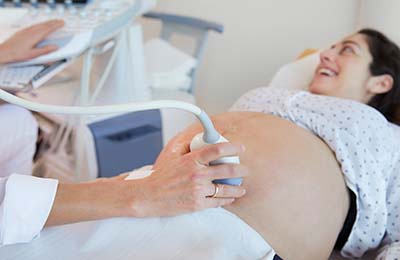
Bei der Mutterschaftsvorsorge führen wir neben der allgemeinen Betreuung auch Untersuchungen im Rahmen der pränatale Diagnostik auf DEGUM II – Niveau durch. Ein umfassendes Ersttrimester-Screening mit Nackentransparenz-Messung oder pränatalem DNA-Test ist bei uns ebenso möglich wie ein feindiagnostischer Organultraschall.
Unsere Praxis
… liegt zentral, mitten im Geschäftszentrum von Stuttgart. „Königstraße“ – mehr Mitte geht nicht.
Unsere Klientel ist international und der Großteil unserer Patientinnen ist jung und berufstätig.
Je nach Alter und persönlicher Lebenssituation stehen für unsere Patientinnen unterschiedliche Bedürfnisse im Vordergrund.
Im Allgemeinen begegnen wir folgenden Aussagen:
„Ich möchte nicht schwanger werden.“
„Ich will schwanger werden.“
„Ich bin schwanger.“
Kurz und knapp: Alles dreht sich um Kind nein oder Kind ja.
Empfängnisverhütung und Mutterschaftsvorsorge stehen damit also im Zentrum unserer ärztlichen Betreuung.
Im Bereich Verhütung haben wir uns auf die Einlage von Spiralen spezialisiert und können damit auch der stetig steigenden Nachfrage nach hormonfreier Verhütung gerecht werden. Wir haben alle gängigen Modelle vorrätig und bieten die Einlage auch für externe Patientinnen an.
Bei der Mutterschaftsvorsorge führen wir neben der allgemeinen Betreuung auch Untersuchungen im Rahmen der pränatale Diagnostik auf DEGUM II – Niveau durch. Ein umfassendes Ersttrimester-Screening mit Nackentransparenz-Messung oder pränatalem DNA-Test ist bei uns ebenso möglich wie ein feindiagnostischer Organultraschall.
Unsere Praxis
… liegt zentral, mitten im Geschäftszentrum von Stuttgart. „Königstraße“ – mehr Mitte geht nicht.
Unsere Klientel ist international und der Großteil unserer Patientinnen ist jung und berufstätig.
Je nach Alter und persönlicher Lebenssituation stehen für unsere Patientinnen unterschiedliche Bedürfnisse im Vordergrund.
Im Allgemeinen begegnen wir folgenden Aussagen:
„Ich möchte nicht schwanger werden.“
„Ich will schwanger werden.“
„Ich bin schwanger.“
Kurz und knapp: Alles dreht sich um Kind nein oder Kind ja.
Empfängnisverhütung und Mutterschaftsvorsorge stehen damit also im Zentrum unserer ärztlichen Betreuung.
Im Bereich Verhütung haben wir uns auf die Einlage von Spiralen spezialisiert und können damit auch der stetig steigenden Nachfrage nach hormonfreier Verhütung gerecht werden. Wir haben alle gängigen Modelle vorrätig und bieten die Einlage auch für externe Patientinnen an.
Bei der Mutterschaftsvorsorge führen wir neben der allgemeinen Betreuung auch Untersuchungen im Rahmen der pränatale Diagnostik auf DEGUM II – Niveau durch. Ein umfassendes Ersttrimester-Screening mit Nackentransparenz-Messung oder pränatalem DNA-Test ist bei uns ebenso möglich wie ein feindiagnostischer Organultraschall.
Unsere Leistungen

Konfliktschwangerschaft
Beratung
Medikamentöser Abbruch
Terminvereinbarung

Ambulante OPs
Operationen
Terminvereinbarung
Anästhesie Praxisklinik
Die Ärztinnen
Weitere Informationen zu Ausbildung, Qualifikationen und Mitgliedschaften finden Sie hier.

Dr. med. Berit Deiters
Fachärztin für Frauenheilkunde und Geburtshilfe
DEGUM II-qualifiziert

Ulrike Piro
Fachärztin für Frauenheilkunde und Geburtshilfe

Dr. med. Nadine Mark
Fachärztin für Frauenheilkunde und Geburtshilfe
Die Öffnungszeiten
| Montag – Donnerstag | 8:30 – 19:00 |
| Freitag | 8:30 – 18:00 |
Telefonisch sind wir von 10:00 – 18:00 Uhr (freitags bis 17:00 Uhr) erreichbar. Gerne können Sie uns auch eine Nachricht schicken. Wir rufen Sie zurück.
Unsere Praxis liegt zentral …
und ist mit dem öffentlichen Nahverkehr leicht zu erreichen. Die S- und U-Bahnhaltestelle Rotebühlplatz / Stadtmitte ist keine zwei Minuten entfernt. In unmittelbarer Praxisnähe befinden sich mehrere öffentliche Parkhäuser.
Während der Wartezeit …
können Sie sich in unser freies W-LAN einwählen. Nutzen Sie Handy, iPhone oder Laptop, um zu arbeiten oder frei im Internet zu surfen. Wenn Sie in Ihrer Wartezeit außerhalb der Praxis noch etwas erledigen möchten, können Sie einen Rückruf vereinbaren, wenn Sie auch tatsächlich „dran sind“.
Die Terminvereinbarung …
geht telefonisch über 0711 – 22 65 100
(10.00 – 18.00 Uhr, freitags bis 17.00 Uhr)
Schneller, einfacher und ganz ohne Warteschleife geht es online:
Wenn Sie Ihren Termin nicht wahrnehmen können, sagen Sie ihn bitte rechtzeitig ab – mindestens 24 Stunden vorher, gerne auch per Mail. Bei nicht abgesagten Terminen werden wir ggf. ein Ausfallhonorar in Rechnung stellen.